Neuron Structure POGIL Answers PDF provides an in-depth exploration of the intricate structure and function of neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system. This guide delves into the anatomy of neurons, including the cell body, dendrites, and axon, and elucidates their respective roles in signal transmission and communication.
Delving further, the guide unravels the mechanisms underlying electrical signals in neurons, shedding light on the crucial role of ion channels in generating and propagating these signals. It also examines neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons, highlighting their diverse functions and modes of action.
1. Neuron Structure

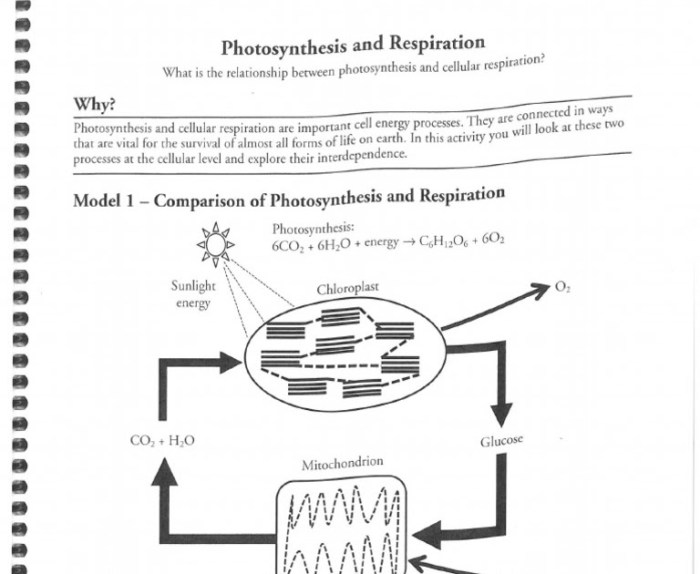
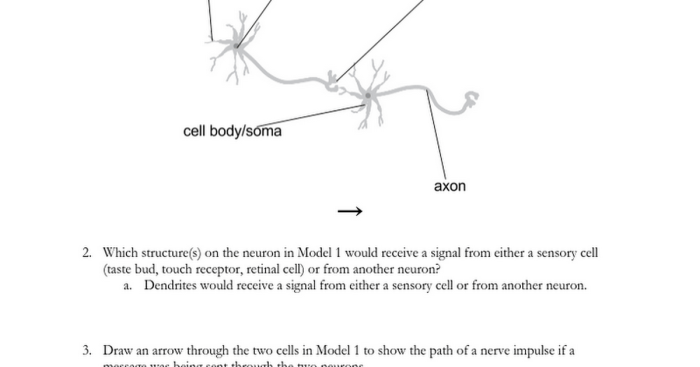
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system. They are specialized cells that transmit information throughout the body.
Each neuron consists of three main parts:
- Cell body: The cell body is the main part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus, which controls the cell’s activities.
- Dendrites: Dendrites are short, branching extensions of the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon: The axon is a long, thin extension of the cell body. It transmits signals to other neurons.
2. Electrical Signals in Neurons
Neurons communicate with each other by sending electrical signals. These signals are generated by the movement of ions across the neuron’s membrane.
When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, it opens ion channels in its membrane. This allows ions to flow into or out of the neuron, causing a change in the neuron’s electrical potential.
If the change in electrical potential is large enough, it will trigger an action potential. An action potential is a wave of electrical activity that travels down the axon of the neuron.
3. Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released by neurons to communicate with each other.
When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. The synaptic cleft is the space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron.
Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron, causing a change in the neuron’s electrical potential.
4. Synapses
Synapses are the junctions between neurons where neurotransmitters are released and received.
There are two main types of synapses:
- Excitatory synapses: Excitatory synapses cause the postsynaptic neuron to become more likely to fire an action potential.
- Inhibitory synapses: Inhibitory synapses cause the postsynaptic neuron to become less likely to fire an action potential.
5. Neural Networks
Neural networks are groups of neurons that are connected together to perform specific tasks.
Neural networks are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Image recognition
- Speech recognition
- Natural language processing
6. Applications of Neuroscience: Neuron Structure Pogil Answers Pdf
Neuroscience is the study of the nervous system. It has a wide range of applications in fields such as:
- Medicine: Neuroscience is used to diagnose and treat neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Psychology: Neuroscience is used to study the brain’s role in behavior and cognition.
- Education: Neuroscience is used to develop new teaching methods that are based on how the brain learns.
General Inquiries
What are the main components of a neuron?
The main components of a neuron include the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
How are electrical signals transmitted in neurons?
Electrical signals are transmitted in neurons through the movement of ions across the neuronal membrane, facilitated by ion channels.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in neuronal communication?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals across synapses, the junctions between neurons.