Related to the pelvic bone crossword – Unveiling the secrets of the pelvic bone, this article embarks on an enlightening journey through its intricate structure, related components, and clinical significance. From its role in supporting the body to its historical and cultural implications, we delve into the fascinating world of this enigmatic bone.
The pelvic bone, a keystone of the skeletal system, plays a pivotal role in maintaining mobility, protecting vital organs, and shaping our understanding of the human body. Its intricate composition and connections with neighboring structures make it a subject of both scientific inquiry and cultural fascination.
Anatomy of the Pelvic Bone: Related To The Pelvic Bone Crossword
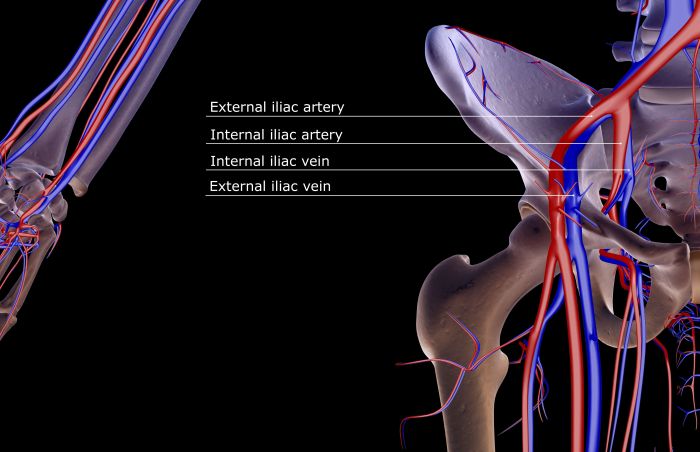
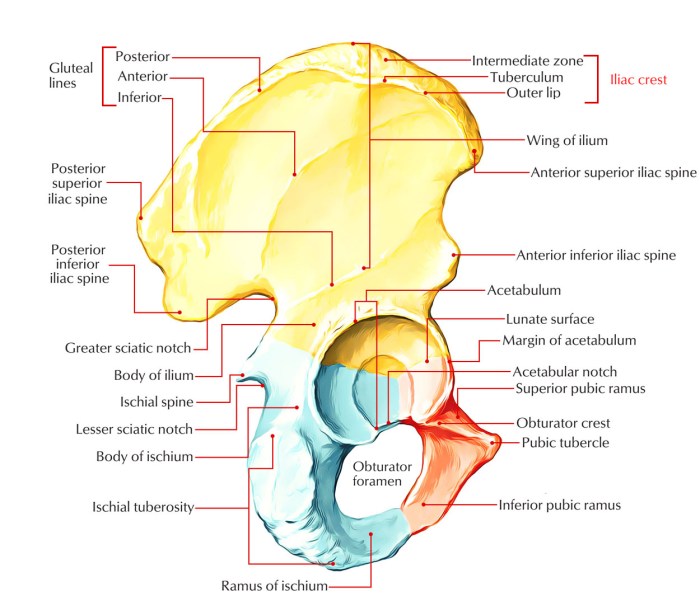
The pelvic bone, also known as the hip bone, is a large, complex structure that forms the bony pelvis. It consists of three main parts: the ilium, the ischium, and the pubis.
Structure and Composition
The pelvic bone is composed of cancellous bone, which is a type of bone that is made up of a network of thin, interconnecting trabeculae. These trabeculae are filled with red bone marrow, which is responsible for producing blood cells.
Parts of the Pelvic Bone
The ilium is the largest and most superior part of the pelvic bone. It forms the upper and lateral portions of the pelvis. The ischium is located below the ilium and forms the posterior and inferior portions of the pelvis.
The pubis is located anteriorly and inferiorly to the ilium and ischium and forms the anterior portion of the pelvis.
Function of the Pelvic Bone
The pelvic bone has several important functions. It supports the weight of the body and protects the organs within the pelvis, including the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs. It also provides attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
Related Structures
The pelvic bone is closely associated with several structures that contribute to its stability and mobility. These include the sacrum, coccyx, and hip joint.
Sacrum
The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the posterior aspect of the pelvis. It is formed by the fusion of five sacral vertebrae and articulates with the ilium of the pelvic bone on either side. The sacrum provides stability to the pelvis and transmits weight from the spine to the pelvic bone.
Coccyx
The coccyx is a small, triangular bone located at the inferior end of the sacrum. It is formed by the fusion of four coccygeal vertebrae and provides attachment for muscles and ligaments that support the pelvic floor.
Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the pelvic bone to the femur (thigh bone). The acetabulum, a socket-shaped cavity in the ilium, receives the head of the femur to form the joint. The hip joint allows for a wide range of motion, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
Pelvic Bone Disorders
Pelvic bone disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the structural integrity and function of the pelvic bones. These disorders can arise from various causes and have significant implications for mobility and overall health.
Common pelvic bone disorders include fractures, dislocations, and arthritis. Fractures occur when the pelvic bone is broken, typically due to high-impact trauma such as falls or accidents. Dislocations involve the displacement of the pelvic bone from its normal position, often caused by sudden forceful movements or injuries.
Arthritis
Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, is a degenerative condition that affects the joints, including those in the pelvis. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Causes:Osteoarthritis can develop due to aging, obesity, joint injury, or genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms:Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion in the affected joint.
- Treatment:Treatment options aim to manage pain and improve mobility. They may include pain relievers, physical therapy, injections, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Pelvic bone disorders can significantly impact mobility and overall health. Fractures can lead to pain, instability, and difficulty walking. Dislocations can cause nerve damage, blood vessel injury, and long-term mobility issues. Arthritis can result in chronic pain, stiffness, and reduced quality of life.
Imaging of the Pelvic Bone
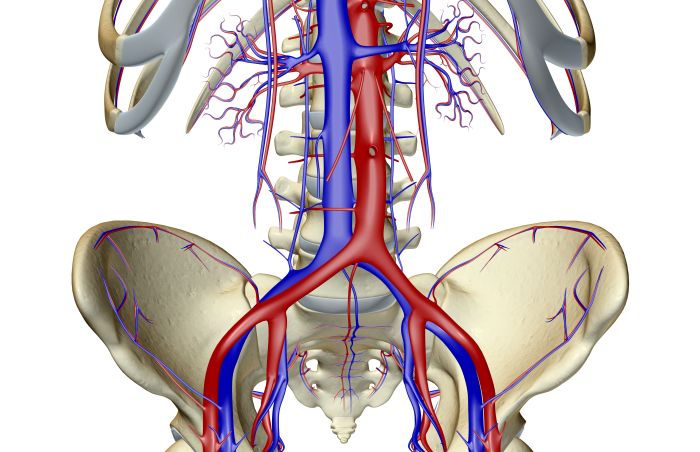
Imaging plays a crucial role in visualizing the pelvic bone, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various disorders. Several imaging techniques are commonly employed for this purpose, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
X-rays
- X-rays are a widely used and readily available imaging technique that provides a two-dimensional view of the pelvic bone.
- They are particularly useful for detecting fractures, dislocations, and other structural abnormalities.
- However, X-rays have limited ability to visualize soft tissues and may not be as sensitive in detecting certain types of pelvic bone disorders.
CT Scans
- Computed tomography (CT) scans utilize X-rays and advanced computer processing to generate cross-sectional images of the pelvic bone.
- CT scans provide more detailed information than X-rays, allowing for better visualization of both bone and soft tissues.
- They are particularly valuable in assessing complex fractures, detecting tumors, and evaluating the extent of pelvic bone disorders.
MRIs
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the pelvic bone and surrounding tissues.
- MRIs are particularly sensitive in detecting soft tissue abnormalities, such as muscle tears, ligament injuries, and tumors.
- They are also useful in evaluating the blood supply to the pelvic bone and assessing the integrity of nerves.
The choice of imaging technique depends on the specific clinical question being addressed. X-rays are often used as an initial screening tool, while CT scans and MRIs may be employed for more detailed evaluations or when soft tissue visualization is necessary.
Imaging plays a vital role in the diagnosis and management of pelvic bone disorders. By providing detailed anatomical information, imaging techniques enable clinicians to accurately assess the extent of injuries, detect underlying abnormalities, and monitor treatment progress.
Pelvic Bone Surgery
Pelvic bone surgery encompasses a range of surgical interventions performed to address various conditions affecting the pelvic bones.
Surgical procedures on the pelvic bone can be broadly categorized into:
- Fracture repair
- Joint replacement
- Tumor resection
Fracture Repair
Pelvic bone fractures, often resulting from high-energy trauma, require surgical intervention to restore bone alignment and stability. Surgical approaches may include:
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF):Direct visualization and alignment of the fracture fragments, followed by stabilization with screws, plates, or rods.
- External fixation:Stabilization of the fracture from outside the body using pins and rods connected to an external frame.
The choice of technique depends on factors such as fracture location, severity, and patient’s overall health.
Joint Replacement
Severe arthritis or other conditions affecting the sacroiliac (SI) joint or hip joint may necessitate joint replacement surgery.
- Sacroiliac joint fusion:Fusing the SI joint to eliminate pain and improve stability.
- Hip replacement:Replacing the damaged hip joint with artificial components.
Tumor Resection
Tumors involving the pelvic bones may require surgical removal to prevent further spread and preserve bone integrity. Surgical approaches include:
- Wide local excision:Removing the tumor along with a margin of surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radical resection:Removing the tumor and a wider margin of surrounding tissue, including adjacent organs or structures.
Postoperative care and rehabilitation following pelvic bone surgery involve pain management, wound care, and physical therapy to restore mobility and function.
Historical and Cultural Significance of the Pelvic Bone
The pelvic bone, with its unique shape and function, has held significant historical and cultural value across various societies.
In ancient Greece, the pelvic bone was revered as a symbol of fertility and childbirth. The goddess Aphrodite, representing beauty and love, was often depicted with a prominent pelvic bone, emphasizing its role in procreation. Similarly, in Roman culture, the pelvic bone was associated with the goddess Venus, the embodiment of beauty and desire.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
In some religious traditions, the pelvic bone is believed to possess spiritual significance. In certain indigenous cultures, the pelvic bone is considered a sacred vessel, representing the connection between the physical and spiritual realms. Rituals and ceremonies often involve the symbolic use of the pelvic bone to invoke divine protection and guidance.
Art and Mythology, Related to the pelvic bone crossword
The pelvic bone has also found its place in art and mythology. In classical sculptures, the pelvic bone is often accentuated to highlight the human form’s beauty and grace. In some myths and legends, the pelvic bone is associated with supernatural powers or divine interventions.
For example, in Norse mythology, the goddess Sif’s golden hair is said to have been made from the pelvic bone of a giant.
Quick FAQs
What is the function of the pelvic bone?
The pelvic bone provides support for the body, protects the organs within the pelvis, and facilitates movement.
What are some common pelvic bone disorders?
Common pelvic bone disorders include fractures, dislocations, and arthritis.
How is the pelvic bone imaged?
The pelvic bone can be imaged using X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
What are the different types of pelvic bone surgery?
Different types of pelvic bone surgery include fracture repair, joint replacement, and tumor resection.