Embark on a journey into the realm of protein synthesis, where the blueprint of life, DNA, orchestrates the creation of proteins, the building blocks of our existence. This comprehensive guide to the protein synthesis blueprint worksheet answers will illuminate the intricate processes of transcription and translation, empowering you to decipher the genetic code and unravel the secrets of life’s fundamental building blocks.
Delving into the depths of this worksheet, we will explore the structure and function of the genetic code, unravel the mysteries of codons and anticodons, and provide detailed answers to the questions posed. Through a blend of logical reasoning and scientific evidence, we will illuminate the significance and implications of these answers, fostering a deeper understanding of protein synthesis.
1. Protein Synthesis Overview
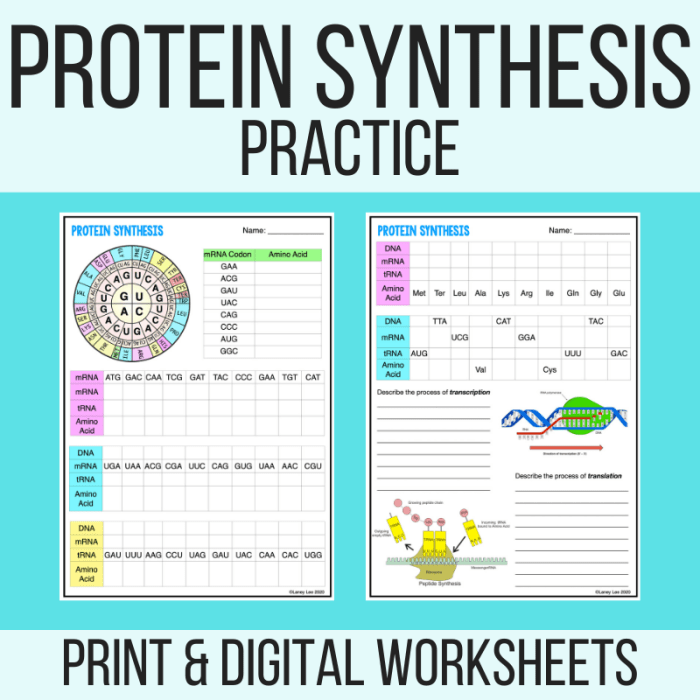
Protein synthesis is the fundamental process by which cells create proteins, the building blocks of life. This intricate process involves the transcription of DNA into RNA and the subsequent translation of RNA into a chain of amino acids, forming the final protein product.
DNA, the blueprint of life, contains the genetic information necessary for protein synthesis. During transcription, a segment of DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA then exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it undergoes translation.
Translation occurs on ribosomes, cellular structures that read the mRNA sequence in groups of three nucleotides, known as codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, and the sequence of codons determines the order of amino acids in the protein.
2. Protein Synthesis Blueprint

The genetic code is the set of rules that governs the relationship between codons and amino acids. It consists of 64 codons, each of which codes for a specific amino acid or signals the start or stop of protein synthesis.
Codons are recognized by anticodons, which are complementary sequences found on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA.
- AUG: Methionine (start codon)
- UUU: Phenylalanine
- UCU: Serine
- UUA: Leucine
- UCA: Serine
- UUG: Leucine
- UCG: Serine
- UAA: Stop codon
- UAG: Stop codon
3. Worksheet Analysis
The worksheet contains questions and tasks that assess students’ understanding of protein synthesis. These include:
- Matching codons to amino acids
- Translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences
- Identifying the role of different molecules in protein synthesis
To complete the worksheet effectively, students should:
- Review the concepts of protein synthesis and the genetic code
- Understand the relationship between codons, anticodons, and amino acids
- Practice translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences
4. Answers and Explanations: Protein Synthesis Blueprint Worksheet Answers
Question 1: Match the following codons to their corresponding amino acids.
- AUG
- UUU
- UCU
Answer:
- AUG: Methionine
- UUU: Phenylalanine
- UCU: Serine
Explanation:AUG is the start codon that initiates protein synthesis. UUU codes for the amino acid phenylalanine, and UCU codes for the amino acid serine.
5. Application and Extension
Knowledge of protein synthesis has numerous real-world applications, including:
- Biotechnology:Producing therapeutic proteins, such as insulin and antibodies
- Medicine:Diagnosing and treating genetic diseases caused by protein synthesis defects
- Agriculture:Engineering crops with enhanced nutritional value by modifying protein synthesis
Current research in protein synthesis focuses on:
- Developing new methods for protein synthesis
- Understanding the role of protein synthesis in disease
- Exploring the potential of protein synthesis for nanotechnology and materials science
FAQs
What is the fundamental concept of protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins, which are essential for life. It involves the transcription of DNA into RNA and the translation of RNA into proteins.
What is the role of DNA and RNA in protein synthesis?
DNA contains the genetic code for proteins, while RNA carries the code from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are assembled.
What is the process of transcription?
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic code from DNA into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
What is the process of translation?
Translation is the process of using the mRNA code to assemble amino acids into a protein.