Embark on an educational journey with our macromolecules word search answer key, a comprehensive guide to understanding the building blocks of life. Dive into the fascinating world of these complex molecules, uncovering their diverse structures, functions, and significance in living organisms.
Macromolecules, the colossal molecules responsible for sustaining life, come in various forms, each playing a crucial role in cellular processes. From the structural support provided by carbohydrates to the genetic blueprints carried by nucleic acids, macromolecules orchestrate the symphony of life.
Macromolecules Overview: Macromolecules Word Search Answer Key
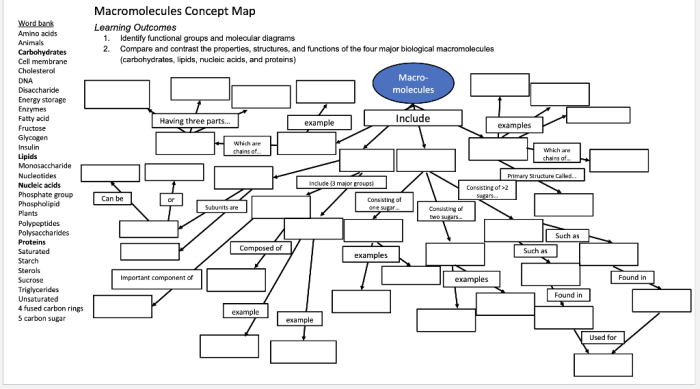
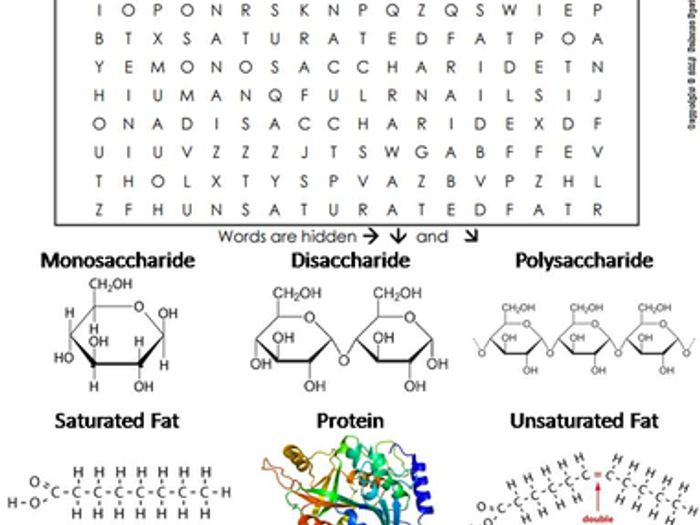
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are essential for life. They are composed of smaller molecules called monomers that are linked together by chemical bonds. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.Carbohydrates are made up of sugars and provide energy for cells.
Proteins are made up of amino acids and perform a variety of functions, including structural support, enzyme catalysis, and hormone regulation. Lipids are made up of fatty acids and are used for energy storage and cell signaling. Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides and store genetic information.
Macromolecule Structures, Macromolecules word search answer key
The molecular structure of macromolecules affects their function. Carbohydrates are typically composed of a chain of sugar molecules, which can be branched or unbranched. Proteins are composed of a chain of amino acids, which are folded into a specific shape.
Lipids are composed of a glycerol molecule attached to two fatty acids. Nucleic acids are composed of a chain of nucleotides, which are arranged in a specific sequence.
Macromolecule Functions
Macromolecules perform a variety of functions in living organisms. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells. Proteins perform a variety of functions, including structural support, enzyme catalysis, and hormone regulation. Lipids are used for energy storage and cell signaling. Nucleic acids store genetic information.
Macromolecule Synthesis and Degradation
Macromolecules are synthesized and degraded by a variety of enzymes. Carbohydrates are synthesized by enzymes called carbohydrases. Proteins are synthesized by enzymes called proteases. Lipids are synthesized by enzymes called lipases. Nucleic acids are synthesized by enzymes called nucleases.
FAQ
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
How do macromolecules interact with each other?
Through various mechanisms, including covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic interactions
What is the role of enzymes in macromolecule metabolism?
Enzymes act as catalysts, facilitating and regulating macromolecule synthesis and degradation