With a flight attendant pulls her 70.0 N at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
This piece delves into the multifaceted world of flight attendants, exploring the physical and mental demands, safety measures, and the intricate balance they maintain while ensuring passenger comfort and well-being.
Occupational Hazards and Safety Measures: A Flight Attendant Pulls Her 70.0 N
Flight attendants face unique occupational hazards due to the physical demands of the job and the environment in which they work. Prolonged standing, irregular sleep patterns, and altitude changes can take a toll on their physical well-being. Additionally, flight attendants must be prepared to respond to emergencies, such as medical incidents, security threats, or aircraft malfunctions.
Physical Hazards
- Prolonged standing can lead to muscle fatigue, joint pain, and varicose veins.
- Irregular sleep patterns can disrupt circadian rhythms, causing fatigue, insomnia, and impaired cognitive function.
- Altitude changes can cause ear pain, sinus pressure, and dehydration.
Safety Measures
To mitigate these hazards, flight attendants undergo rigorous safety training and follow established safety protocols. They are equipped with personal protective equipment, such as life vests and oxygen masks, and are trained to perform emergency procedures. Regular health screenings and access to occupational health services help ensure the well-being of flight attendants.
Physical and Psychological Effects of the Job
The physical and psychological demands of being a flight attendant can have significant effects on their health and well-being.
Physical Effects
- Musculoskeletal disorders:Prolonged standing and lifting heavy bags can lead to muscle strain, back pain, and other musculoskeletal issues.
- Cardiovascular problems:Irregular sleep patterns and high levels of stress can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Gastrointestinal issues:Changes in altitude and irregular eating habits can cause digestive problems, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Psychological Effects
- Fatigue:Long hours, irregular sleep patterns, and jet lag can lead to chronic fatigue.
- Stress:Dealing with demanding passengers, handling emergencies, and working in a confined space can be stressful.
- Isolation:Spending long periods away from home and working with different crews can lead to feelings of isolation.
Coping Mechanisms
Flight attendants employ various coping mechanisms to manage the physical and psychological effects of their job, including:
- Regular exercise and healthy eating
- Getting enough sleep and practicing relaxation techniques
- Seeking support from colleagues, family, and friends
Training and Certification Requirements
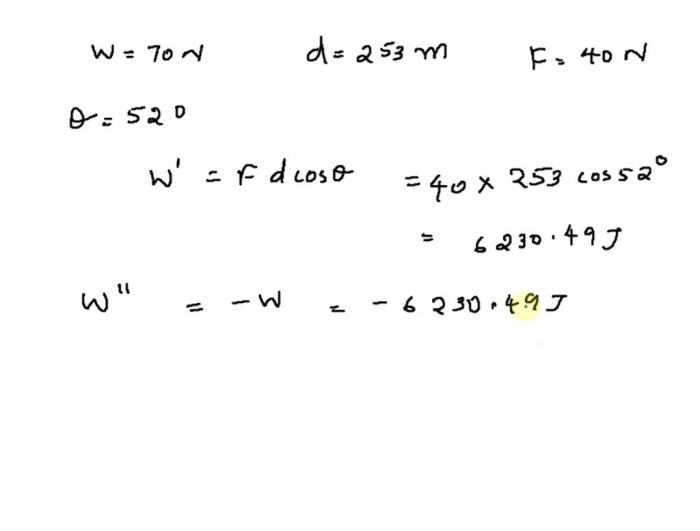
Becoming a flight attendant requires specialized training and certification. Applicants typically undergo a rigorous screening process that includes background checks, physical exams, and interviews.
Training
Flight attendant training typically lasts for several weeks and covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Safety procedures and emergency response
- Customer service and interpersonal skills
- Aircraft operations and procedures
- First aid and medical emergencies
Certification
Upon successful completion of training, flight attendants must obtain certification from the relevant regulatory authority, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States. Certification requires passing a written exam and a practical demonstration of skills.
Ongoing Training
Flight attendants are required to undergo ongoing training to maintain their skills and knowledge. This includes regular refresher courses, emergency drills, and specialized training for specific aircraft types.
Customer Service and Interpersonal Skills
Flight attendants play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and comfort of passengers. They must possess excellent customer service and interpersonal skills to effectively interact with passengers and handle challenging situations.
Customer Service Skills
- Communication:Flight attendants must be able to communicate clearly and effectively with passengers from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
- Empathy:They must be able to understand and respond to the needs of passengers, including those with disabilities or special requirements.
- Problem-solving:Flight attendants must be able to resolve passenger issues quickly and efficiently.
Interpersonal Skills
- Teamwork:Flight attendants work closely with other crew members, including pilots, cabin crew, and ground staff.
- Conflict resolution:They must be able to handle difficult passengers and de-escalate conflicts.
- Cultural sensitivity:Flight attendants must be aware of and respectful of different cultures and customs.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Flight attendants are trained to respond to a wide range of emergencies, including medical emergencies, security threats, and aircraft malfunctions.
Emergency Procedures, A flight attendant pulls her 70.0 n
Flight attendants are trained in specific emergency procedures, such as:
- Evacuating passengers from the aircraft
- Providing first aid and medical assistance
- Handling security threats
- Operating emergency equipment
Response Training
Flight attendants undergo regular emergency response training to ensure their skills and knowledge are up-to-date. This training includes simulations and exercises that test their ability to respond effectively to various emergency scenarios.
Examples of Emergency Response
Flight attendants have a proven track record of successfully handling emergencies. For example, in 2020, flight attendants on a Southwest Airlines flight successfully evacuated all 149 passengers and crew members after the aircraft’s engine exploded mid-flight.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook

The flight attendant industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing passenger expectations.
Current Trends
- Increased use of technology:Flight attendants are using mobile devices and other technologies to improve customer service and streamline operations.
- Focus on passenger experience:Airlines are investing in training and initiatives to enhance the passenger experience.
- Changing demographics:The flight attendant workforce is becoming more diverse in terms of age, gender, and cultural background.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the flight attendant profession is positive. The industry is expected to grow as air travel demand increases. Flight attendants will continue to play a vital role in ensuring the safety and comfort of passengers.
Skills and Qualities in Demand
Flight attendants with the following skills and qualities will be in high demand in the future:
- Excellent customer service skills
- Strong interpersonal skills
- Ability to work in a team environment
- Cultural sensitivity
- Knowledge of new technologies
FAQs
What are the common physical hazards faced by flight attendants?
Prolonged standing, irregular sleep patterns, altitude changes, and exposure to radiation are some of the common physical hazards faced by flight attendants.
How do flight attendants maintain their well-being despite the demanding nature of their job?
Flight attendants employ various coping mechanisms and strategies to maintain their well-being, such as regular exercise, healthy eating habits, and seeking support from colleagues and family.