Embark on a historical journey with the Empire of Mali Worksheet Answer Key, a comprehensive guide to unlocking the secrets of this influential West African empire. Dive into its captivating timeline, explore its vast geographical reach, and unravel the intricacies of its economic, social, and cultural tapestry.
From the rise of legendary rulers to the empire’s architectural wonders, this answer key provides a comprehensive understanding of the factors that shaped the Empire of Mali’s grandeur and eventual decline. Prepare to delve into a world of rich history and cultural heritage, gaining invaluable insights into one of Africa’s most enduring empires.
Historical Overview of the Empire of Mali

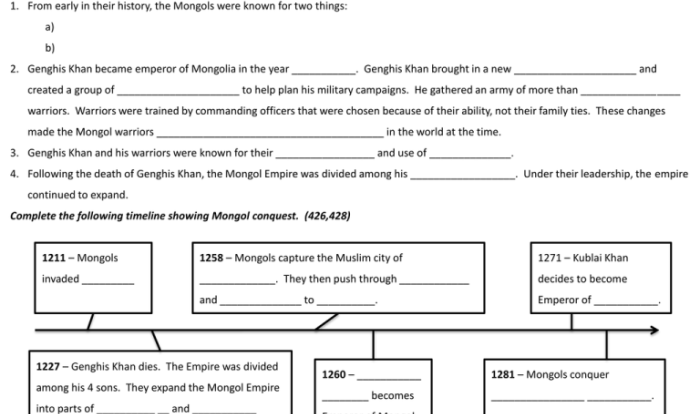
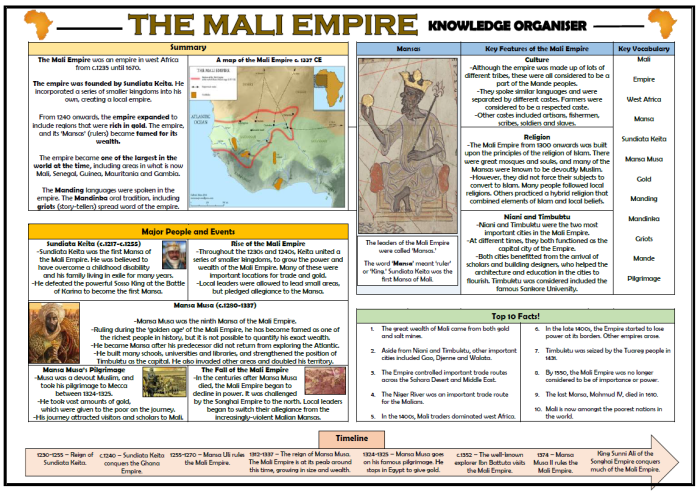
The Empire of Mali, renowned as one of the most prominent and prosperous empires in African history, emerged in the 13th century in West Africa. Its origins can be traced back to the Kingdom of Kangaba, founded by the Mande people in the 11th century.
The empire’s rise to prominence was marked by a series of influential rulers who played pivotal roles in shaping its destiny.
Key Rulers and their Contributions
- Sundiata Keita (c. 1215-1255): Known as the “Lion King of Mali,” Sundiata Keita is credited with founding the Mali Empire in 1235. He led the Mande people to victory against the Sosso Empire at the Battle of Kirina in 1235, establishing the Mali Empire’s dominance in the region.
- Mansa Musa (c. 1312-1337): Mansa Musa’s reign marked the pinnacle of Mali’s power and wealth. He was renowned for his extravagant pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324, during which he distributed vast amounts of gold, earning him the title “King of Gold.” His reign also witnessed significant advancements in trade, architecture, and education.
- Mansa Suleiman (c. 1341-1360): Mansa Suleiman succeeded Mansa Musa and continued his legacy of prosperity. He expanded the empire’s territories and fostered diplomatic relations with neighboring kingdoms. Under his rule, Timbuktu emerged as a renowned center of learning and culture.
Geographical Extent and Influence: Empire Of Mali Worksheet Answer Key
The Empire of Mali reached its peak during the reign of Mansa Musa in the 14th century. At its greatest extent, it encompassed a vast territory stretching from the Atlantic coast in the west to the present-day Niger River in the east, and from the Sahara Desert in the north to the rainforests of Guinea in the south.
The empire’s strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes made it a hub for commerce and cultural exchange. Mali’s control over the trans-Saharan trade routes enabled it to dominate the flow of gold, salt, and other goods between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
The empire also played a significant role in the spread of Islam and Arabic culture throughout West Africa.
Influence on Trade, Empire of mali worksheet answer key
The Empire of Mali’s control over the trans-Saharan trade routes gave it a monopoly on the flow of gold and salt between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa. This monopoly allowed the empire to accumulate immense wealth and power.
- The empire’s control over the gold trade made it one of the richest and most powerful empires in Africa.
- The empire’s wealth allowed it to patronize the arts and sciences, and to build magnificent cities such as Timbuktu.
- The empire’s control over the salt trade gave it a strategic advantage over its neighbors.
Influence on Cultural Exchange
The Empire of Mali was a major center of Islamic scholarship and learning. The empire’s rulers were patrons of the arts and sciences, and they encouraged the development of a rich cultural tradition.
- The empire’s rulers founded universities and libraries, and they attracted scholars from all over the Islamic world.
- The empire’s cultural influence spread throughout West Africa, and it played a major role in the development of the region’s cultural heritage.
- The empire’s cultural influence is still evident today in the region’s music, art, and architecture.
Economic and Social Structure
The Empire of Mali’s economic prosperity was driven by its control over key trade routes, particularly the trans-Saharan trade between North Africa and West Africa. The empire served as a hub for the exchange of goods such as gold, salt, ivory, and slaves.
The social hierarchy of the Empire of Mali was complex, with the emperor, known as the mansa, at the apex. Below the mansa were various classes of nobles, officials, and commoners. The nobility included the king’s relatives, military leaders, and provincial governors.
The officials were responsible for administering the empire’s vast territory, while the commoners formed the majority of the population and were engaged in agriculture, trade, and crafts.
Economic Activities
- Agriculture:The empire’s primary economic activity was agriculture, with crops such as millet, sorghum, and rice being cultivated.
- Trade:The empire’s control over the trans-Saharan trade routes made it a major hub for the exchange of goods between North Africa and West Africa. Gold, salt, ivory, and slaves were among the most important commodities traded.
- Mining:The empire was also rich in mineral resources, including gold, which was mined in the Bambuk region.
Social Hierarchy
- Emperor (Mansa):The emperor was the supreme ruler of the empire and held absolute power.
- Nobility:The nobility included the emperor’s relatives, military leaders, and provincial governors.
- Officials:The officials were responsible for administering the empire’s vast territory and included judges, tax collectors, and market inspectors.
- Commoners:The commoners formed the majority of the population and were engaged in agriculture, trade, and crafts.
- Slaves:Slaves were a significant part of the empire’s social structure and were used for a variety of purposes, including labor and military service.
Cultural Achievements
The Empire of Mali was renowned for its impressive architectural and artistic achievements, showcasing the empire’s wealth and cultural sophistication. The most notable architectural feats were the grand mosques constructed in the major cities, particularly the Great Mosque of Djenné.
This iconic structure is renowned for its intricate mud-brick construction, towering minarets, and unique pyramidal design. Other notable architectural achievements include the Sankore Madrasah in Timbuktu, a renowned center of Islamic learning, and the ruins of the ancient city of Gao.Religion
played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural development of the Empire of Mali. Islam was the dominant religion, and its influence is evident in the empire’s architecture, art, and intellectual pursuits. The establishment of Timbuktu as a major center of Islamic scholarship attracted scholars and students from across the Muslim world, contributing to the empire’s reputation as a hub of knowledge and learning.
Education was highly valued in Mali, with Timbuktu becoming a renowned center for the study of Islamic law, astronomy, and other subjects. The empire’s cultural achievements extended beyond religion, with the development of a rich oral tradition that included epic poems, stories, and songs that celebrated the empire’s history and heroes.
Artistic Achievements
The Empire of Mali fostered a vibrant artistic culture, producing exquisite works of art that showcased the empire’s wealth and cultural sophistication. Goldsmiths crafted intricate jewelry and ornaments, while skilled weavers produced finely woven textiles. The empire was also renowned for its production of leather goods, particularly its embossed and tooled leatherwork.
The artisans of Mali demonstrated their mastery in the creation of musical instruments, such as the kora, a stringed instrument that became an integral part of the empire’s musical traditions.
Decline and Fall of the Empire
The Empire of Mali, once the largest and most prosperous empire in West Africa, began to decline in the 14th century. Several factors contributed to its downfall, including:
-
-*Internal conflicts
After the death of Mansa Musa, the empire was plagued by internal conflicts between rival factions. These conflicts weakened the central authority and led to the fragmentation of the empire.
-*External threats
The empire faced increasing pressure from external threats, such as the rise of the Songhai Empire to the east and the Moroccan invasion of 1352. These threats diverted resources from internal development and further weakened the empire.
-*Economic decline
The empire’s economy was heavily dependent on the trans-Saharan trade. However, the rise of new trade routes and the decline of the gold trade led to a decrease in revenue. This economic decline further weakened the empire and made it more vulnerable to external threats.
Legacy and Impact
Despite its decline, the Empire of Mali left a lasting legacy on West African history. The empire’s achievements in trade, culture, and administration influenced the development of subsequent West African states. The empire’s legacy can be seen in:
-
-*The spread of Islam
The empire played a major role in the spread of Islam throughout West Africa. Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 brought Mali to the attention of the Muslim world and helped to establish Islam as the dominant religion in the region.
-*The development of trade
The empire’s trans-Saharan trade routes facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between West Africa and the rest of the world. This trade brought wealth and prosperity to the empire and helped to stimulate the development of urban centers.
-*The rise of new empires
The decline of the Empire of Mali created a power vacuum in West Africa. This vacuum was filled by the rise of new empires, such as the Songhai Empire and the Kingdom of Benin. These empires built upon the legacy of Mali and continued to play a major role in West African history.
Educational Resources
The Empire of Mali has been a subject of extensive research and documentation, resulting in a wide range of educational resources available for further exploration. These resources provide valuable insights into the empire’s history, culture, and legacy.
Books
- The Empire of Mali: A History of Power and Identityby Nehemia Levtzion and Randall Pouwels: This comprehensive book offers a detailed overview of the empire’s political, economic, and cultural development.
- The Cambridge History of Africa: Volume 3, From c. 1050 to c. 1600by Roland Oliver and Anthony Atmore: This volume includes a chapter dedicated to the Empire of Mali, providing a scholarly analysis of its history and impact.
- Mansa Musa of Mali: Pilgrimage of an African Kingby Thomas B. Finkenauer: This book focuses on the famous pilgrimage of Mansa Musa, exploring its religious, political, and economic significance.
Articles
- “The Empire of Mali: A West African Powerhouse” by Smithsonian Magazine: This article provides a concise and accessible introduction to the empire’s history and achievements.
- “The Economic and Social Structure of the Empire of Mali” by Patrick Manning: This scholarly article examines the economic and social systems that supported the empire’s growth and prosperity.
- “The Cultural Legacy of the Empire of Mali” by David Conrad: This article highlights the empire’s contributions to architecture, literature, and the arts.
Documentaries
- The Empire of Maliby History Channel: This documentary provides a visual overview of the empire’s history, culture, and legacy.
- Mansa Musa: The Richest Man in Historyby BBC: This documentary focuses on the life and reign of Mansa Musa, exploring his pilgrimage and its impact on the empire.
- The Kingdoms of West Africaby National Geographic: This documentary includes a segment on the Empire of Mali, showcasing its architectural achievements and economic power.
These educational resources offer a comprehensive and accessible way to explore the fascinating history and legacy of the Empire of Mali. They provide valuable insights into the empire’s political, economic, social, and cultural achievements, enabling a deeper understanding of its significance in African and world history.
Interactive Activities
Interactive activities provide an engaging and dynamic way for students to learn about the Empire of Mali. These activities can enhance understanding, foster critical thinking, and promote collaboration.
Multiple-Choice Quiz
Design a multiple-choice quiz that covers key aspects of the Empire of Mali’s history, geography, and culture. This quiz can assess students’ knowledge and identify areas for further exploration.
Interactive Map
Create an interactive map that allows students to explore the geographical extent and influence of the Empire of Mali. The map can include historical markers, timelines, and interactive elements that provide additional information.
Discussion Forum
Establish a discussion forum where students can share their perspectives on the Empire of Mali’s history and significance. Encourage students to engage in respectful and informed discussions, fostering a deeper understanding of the empire’s impact.
FAQ Insights
What was the geographical extent of the Empire of Mali at its peak?
At its peak, the Empire of Mali stretched from the Atlantic coast in the west to the Niger River in the east, and from the Sahara Desert in the north to the rainforests of Guinea in the south.
Who was the most famous ruler of the Empire of Mali?
Mansa Musa, who ruled from 1312 to 1337, is considered the most famous ruler of the Empire of Mali. He was known for his wealth, piety, and patronage of the arts.
What were the major economic activities of the Empire of Mali?
The major economic activities of the Empire of Mali included trade, agriculture, and mining. The empire was a major trading center for gold, salt, and other goods.
What were the major cultural achievements of the Empire of Mali?
The major cultural achievements of the Empire of Mali included the construction of the Great Mosque of Djenné, the development of a written script, and the patronage of scholars and artists.
What factors contributed to the decline of the Empire of Mali?
The factors that contributed to the decline of the Empire of Mali included internal conflicts, external invasions, and economic decline.